That's why we created deep search, a new Microsoft Bing feature that provides even more relevant and comprehensive answers to the most complex search queries. Deep search is not a replacement for Bing's existing web search, but an enhancement that offers the option for a deeper and richer exploration of the web.

Understanding search intent
Deep search builds on Bing's existing web index and ranking system and enhances them with GPT-4. GPT-4 is a state-of-the-art generative AI LLM (Large Language Model) that can create natural language text from any input. In the case of deep search, GPT-4 takes the search query and expands it into a more comprehensive description of what an ideal set of results should include.For example, let’s say I’m researching loyalty programs in different countries and search for "how do points systems work in Japan". Deep search might generate a more comprehensive description like this:
Provide an explanation of how various loyalty card programs work in Japan, including the benefits, requirements, and limitations of each. Include examples of popular loyalty cards from different categories, such as convenience stores, supermarkets, and restaurants. Show a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of using loyalty cards versus other payment methods in Japan, including current rewards and benefits. Highlight the most popular services and participating merchants.
This expanded description captures my intent and expectations more accurately and clearly than a few keywords. It also helps Bing understand what kind of information I am looking for.
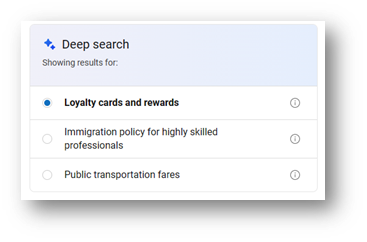
Some queries are ambiguous. For example, "how do points systems work in Japan" could refer to rewards points, as I intended, but could also be seeking information on immigration policy or something else. The expanded description may be right for one of those interpretations but not for all of them. In that case, deep search leverages GPT-4 to find all the possible intents and computes an comprehensive description for each of them. Deep search offers a disambiguation pane where all of these intents are represented. If my research intent was misunderstood, I can select the right one from the disambiguation pane, and the corresponding comprehensive description will be used instead.
Finding deeper results
Bing then goes much deeper into the web with that task in mind, pulling back relevant results that often don't show up in typical search results. Deep search uses a combination of querying techniques to find pages that might match my expanded query, rewriting the query on my behalf, and searching for those variations too.For example, for my earlier loyalty points query, deep search might also try searching for:
- loyalty card programs Japan
- best loyalty cards for travelers in Japan
- comparison of loyalty programs by category Japan
- redeeming loyalty cards in Japan
- managing loyalty points with phone apps
Ranking results
Once deep search has gathered a wide collection of web pages to review, it then ranks them according to how well they match the comprehensive description. Deep search uses a variety of signals to determine the relevance and quality of each result, considering factors like how well the topic matches, whether it’s at the appropriate level of detail, how credible and trustworthy the source is, how fresh and popular it is, and so on.By doing this, deep search can present a curated list of results and answers that are more likely to answer your question, satisfy your curiosity, or solve your problem.
Speed
Going deeper takes time, and deep search can take up to thirty seconds to complete. This might seem like a long time compared to normal search, but it can be worth the wait for more specific or comprehensive answers.Deep search is not meant for every query or every user. It's designed for those who have complex questions that require more than a simple answer. Bing will always return regular search results in less than a second and deep search is an optional feature.
More ways that GPT-4 is used in Bing
GPT-4 is already used in many places on Bing, including Copilot, Image Creator from Designer, and already in regular web result ranking where, in January, it powered one of the single biggest relevance improvements in Bing’s history.We’re excited for the potential for deep search to offer yet another significant improvement in search result quality. This is currently an experimental feature that is available to randomly selected small groups of users on Bing worldwide while we are testing and improving it. We would love to hear your feedback and suggestions on how to make deep search better.
